- Home
- Worldwide
- Our regional offices
- Central Africa
- Congo
Congo
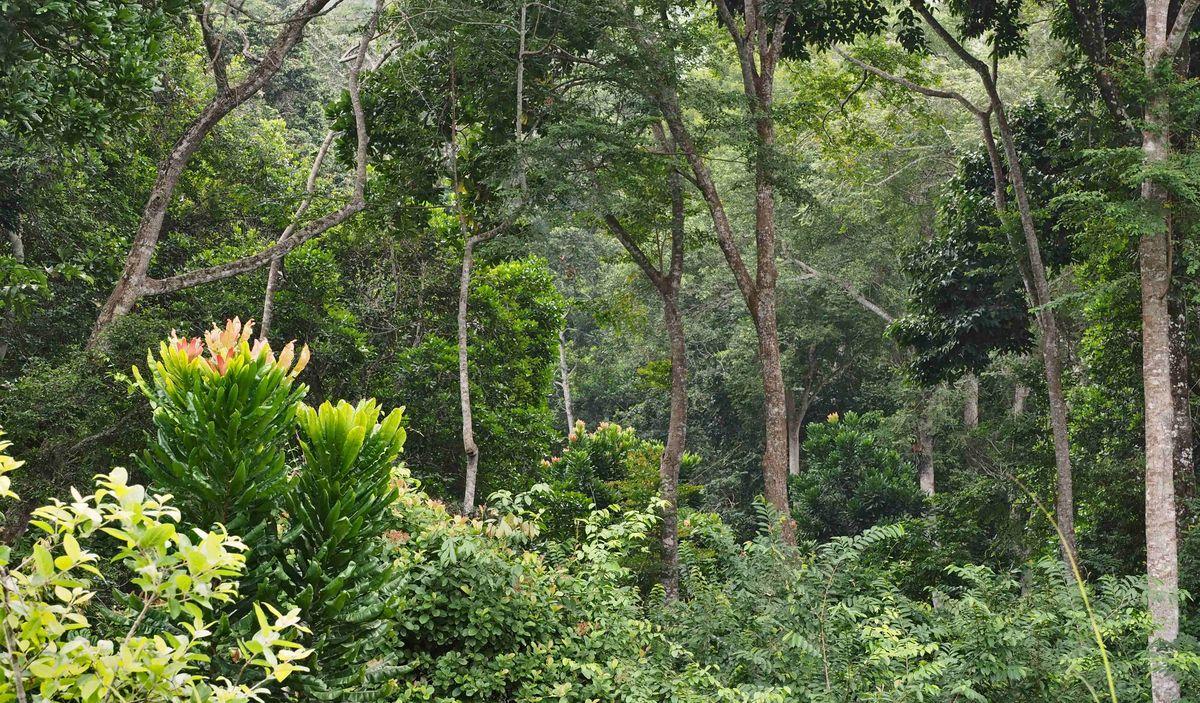

Dense forest in northern Congo © Y. Van Hoef, CIRAD
The forestry sector plays a major role in Congo’s agricultural economy
Since 2014, the Congolese economy has been affected by a significant drop in public revenue, due to a collapse in the price of oil, which nonetheless remains dominant in the country’s GDP (40%) and its exports (over 80%). Agriculture remains underdeveloped, but in this difficult economic context it is experiencing renewed interest and has become a priority in the government’s roadmap. The National Development Programme (PND) is seeking to diversify and improve agricultural productivity, professionalize the sector, revive major food and commercial value chains, and to invest in and develop agroindustry, etc. To that end, some major programmes have been launched, including the Sustainable Land Use Programme (PUDT) backed by the Central African Forest Initiative (CAFI). Although the forestry sector remains a major player in the country’s economy, the rich biodiversity of its forests and its vast peatlands are major conservation issues.
CIRAD’s main activities and missions in Congo
In terms of climate change, sustainable management of natural resources, especially forests (forests occupy almost two thirds of national territory), remains one of the country’s major development challenges. Conserving biodiversity and fragile ecosystems such as peatlands – a carbon sink of considerable volume covering almost 150 000 km² - lies at the heart of environmental concerns. Several projects, either under way or on the drawing board, are focusing on the dynamics and functioning of forest ecosystems and on establishing plantations of local forest species, along with agroforests.
As regards sustainable forest management and integrated land management, animal health, disease surveillance and the One Health approach, research and training, and more generally institutional capacity building, are of particular importance.
Key figures
- 4 researchers on overseas postings
- 15 to 20 missions per year
- 4 current projects
- 5 PhD students supervised
Main research areas
- Sustainable management of forest resources
- Human health/wildlife relations, zoonosis prevention
- Land use planning and sustainable agriculture
Platforms in partnership
Congo, with IRF and UMNG, is a partner of the R2FAC research and training platform in partnership (dP) (founding members).
Main partners
Ministries, research and development organizations, and universities
- Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technological Innovation (MESRSIT):
- Marien Ngouabi University (UMNG), including its Faculty of Science & Technology (FST) and its Ecole Normale Supérieure (ENS)
- National Forestry Research Institute (IRF)
- National Agricultural Research Institute (IRA)
- Research Centre on the Sustainability of Industrial Plantation Productivity (CRDPI)
- Ministry of Forest Economy (MEF)
- Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries, including the General Directorate of Livestock (DGE)
- Ministry of Health and Population including the National Public Health Laboratory (LNSP)