Just out 30 January 2026
- Home
- CIRAD news
- News
- Economics of pastoralism
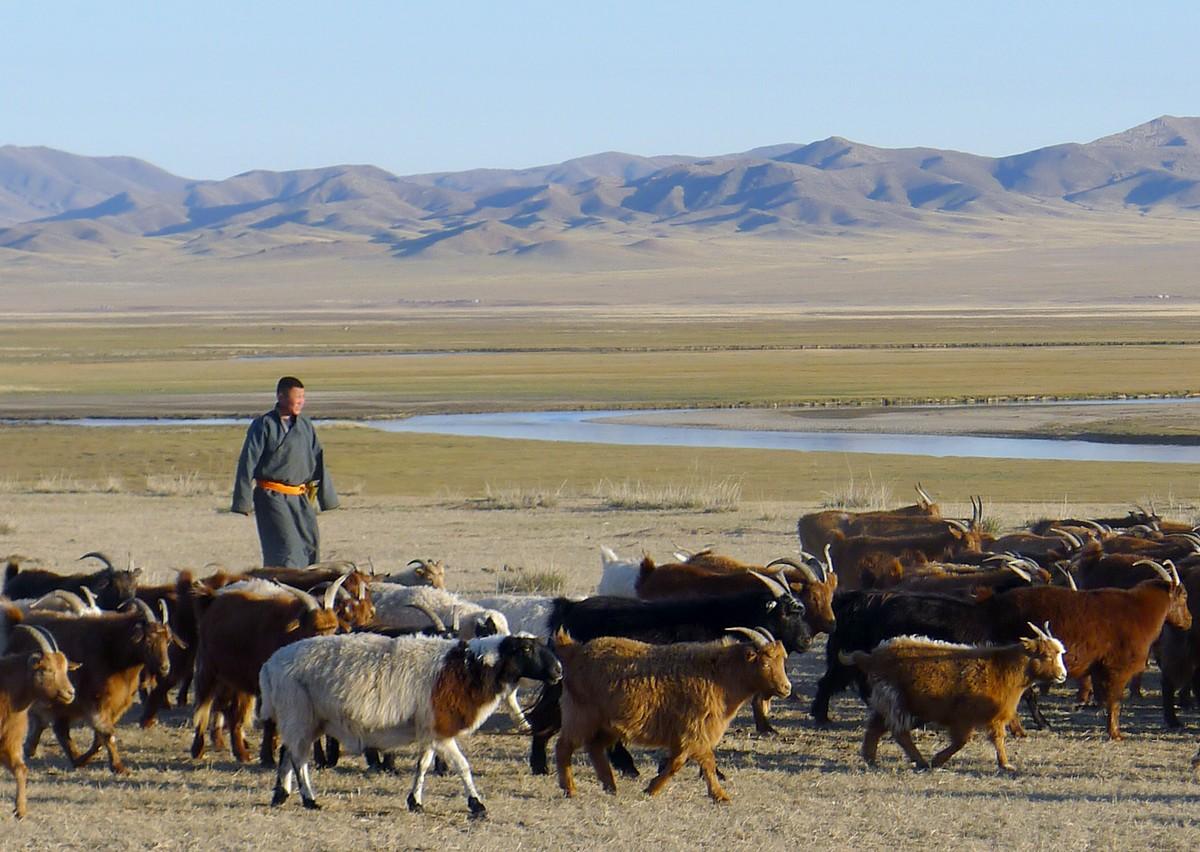
Pastoralism | An underestimated contribution to national economies
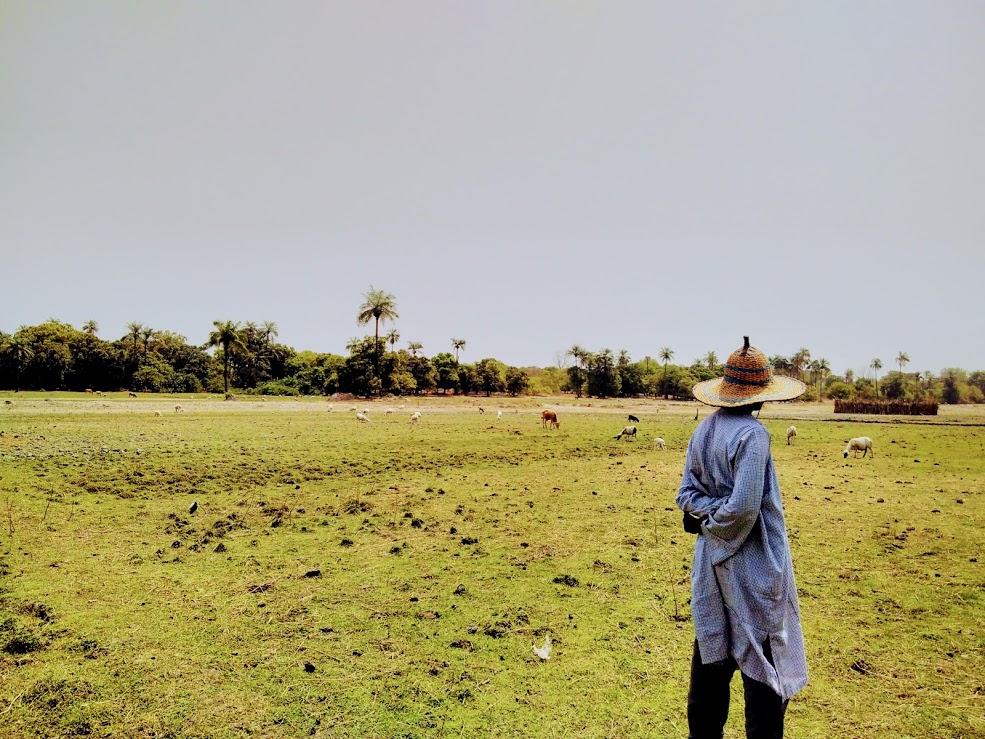

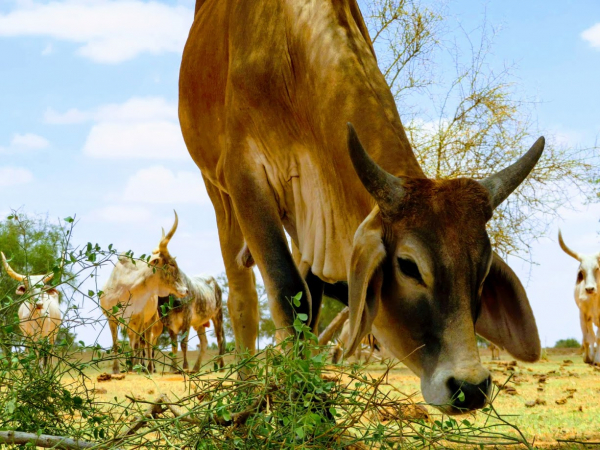
All over the world, pastoralism is the main source of agricultural revenue in arid, cold and mountainous zones. However, public- and private-sector players often overlook its importance. For Abdrahmane Wane, an economist with CIRAD who coordinated the study, "this lack of consideration stems primarily from a lack of knowledge and awareness of the multifunctionality of pastoral livestock farming, notably in terms of its role in supplying animal products, in food and nutrition security, job creation, biomass production and biodiversity conservation, and in the water cycle".
Knowing more about pastoral activities, to support them more effectively
Taking Argentina, Chad and Mongolia as pilot cases, the study set out to fill in the gaps in knowledge, notably by quantifying certain economic aspects. Improving knowledge of pastoral systems would enable governments to invest in helping those systems respond better to growing demand for animal products and provide them with the services, infrastructures and land security they need. The study was commissioned by FAO, funded by IFAD and conducted by CIRAD, with valuable contributions from national and regional pastoral associations, which were closely involved in gathering information and in primary data analyses.
Pastoralism produces wealth
Pastoral households in the three countries studied contribute to national wealth creation. Due to the extent of self-consumption, particularly in Argentina and Chad, the contribution farmers make to national economies is largely underestimated. Allowing for self-consumption, livestock farmers account for 1.4% of gross domestic product (GDP) in Argentina, 11.9% in Mongolia and a whopping 27% in Chad.
A major challenge: high levels of inequality
One point shared by the three countries is the high level of inequality in pastoral communities. This is the result of major disparities in terms of land use, and raises the issue of access to productive resources land, natural resources, basic social services, infrastructures, etc).
Persistent inequalities can threaten the growth of the sector, trigger political and economic instability and thus reduce investment, and fuel social resentment and protectionism.
Pastoralism is a master of adaptation
Livestock farmers live in an uncertain environment prone to various types of shocks. Their successful adaptation strategies depend on the possibilities available to them: mobility, family labour, sales of animals, etc. And contrary to popular myth, all the livestock farmers questioned relied primarily on their family resources and their social capital. They did not see official support as a preferred strategy.
For an observatory of pastoralism
To visualize the different contributions and the requirements of pastoral activities, the researchers involved in the study recommend setting up observatories of pastoralism. Observatories would boost confidence between stakeholders in the sector and thus enable real-time data gathering, and simulations to describe the main socioeconomic and environmental trends. They would rely on and facilitate the establishment of a network of partners devoted to the development of pastoralism, largely founded on pastoral organizations. "The study gave very promising results in this respect, since the agropastoral associations involved were very committed and entirely capable of coping with a range of data gathering and management tasks", Abdrahmane Wane stresses. "Moreover, they play a determining role in policy dialogue."
Migration of young pastoral farmers to urban areas
FAO also recently published "Jeunes pasteurs en ville", a series of surveys of the pathways followed by young people from pastoral environments and their context, in Burkina Faso and Chad. The work was coordinated by CIRAD's Véronique Ancey, who is currently on assignment to FAO as an expert in livestock and poverty reduction in arid zones.Those young people's life stories reflect the challenge for families of reconciling mobility and attachment to their home area. They also bear witness to the emergence in Burkina Faso of claims not just to productive rights, but also to civil rights, from historically politically marginalized population groups.The report's conclusions and the reception it received have triggered a collaboration between FAO, the public authorities and pastoral organizations in the Sahel, aimed at rebuilding a social contract centring on pastoralism, notably by extending social protection to pastoral communities.