Call to action 16 April 2025
- Home
- Press area
- Press releases
- Tree crops, sustainable crops
Tree crops, a vital lever for meeting the Sustainable Development Goals
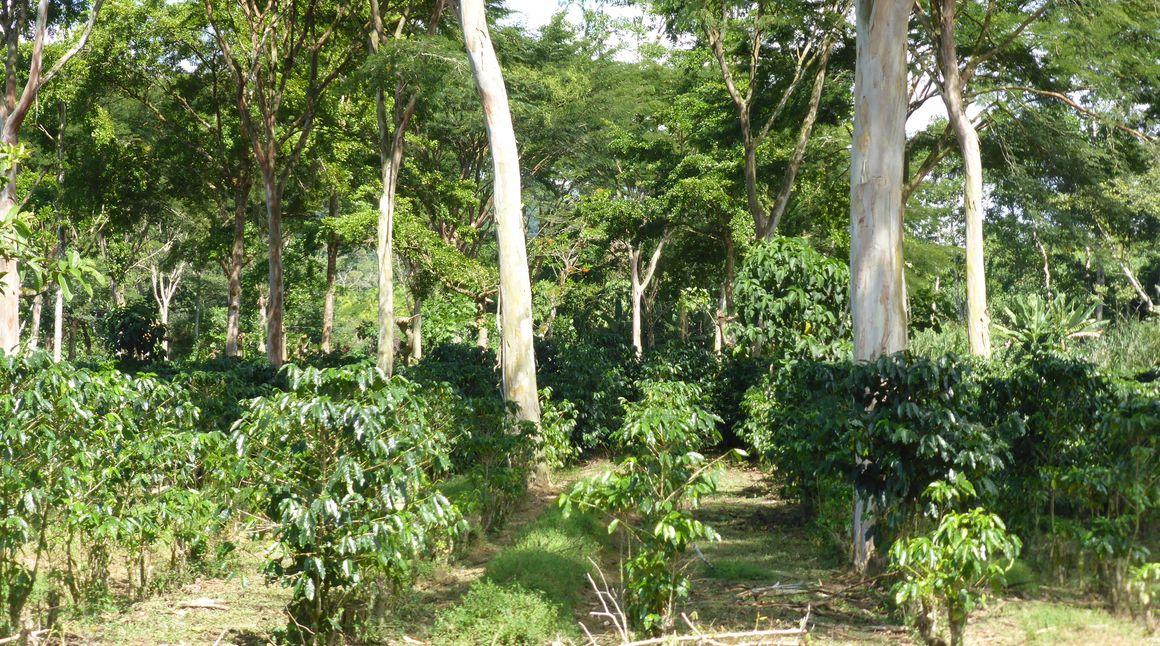

A coffee-based agroforestry system in Costa Rica © J. Avelino, CIRAD
Tree crops such as olive, coffee, cocoa and fruit trees cover more than 183 million hectares worldwide. However, they have been largely left out of agricultural policy, in spite of their vital role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). An article in Nature Sustainability by an international team coordinated by the Estación Biológica de Doñana (CSIC) in Seville (Spain) highlights the fact that such crops are not just crucial for global food supplies and the global economy, but also have huge potential to protect biodiversity, mitigate climate change and improve living conditions for millions of people worldwide.
"We are missing a major opportunity to use tree crops to tackle some of the major environmental and social challenges of our time", says Carlos Martínez-Núñez, a researcher at the Estación Biológica de Doñana who coordinated the study. "Provided they are managed correctly, these types of farming systems can be a powerful tool for conserving biodiversity, mitigating the effects of climate change and alleviating rural poverty, as well as producing some 1000 million tonnes of food a year."
"This is particularly true for coffee and cocoa agroforestry systems in tropical and equatorial zones", CIRAD's Jacques Avelino and Martijn ten Hoopen, co-authors of the article, explain. "Unfortunately, the price volatility surrounding these products has triggered recurrent social and ecological crises. When returns are poor, these systems are either abandoned or replaced by other, less ecofriendly crops, or on the contrary intensified to make them more profitable, at the expense of the environment."
The conclusions of the study suggest that policymakers should draft a specific strategy to promote more sustainable practices for such crops. Agricultural policies generally focus on annual crops such as wheat, sunflower or rice, whose life cycle, from germination to reproduction, is completed within a year. Although it is vital to promote sustainable practices for annual crops, their ecological benefits are often limited by their simple structure and short-term dynamic. Tree crops, on the other hand, are more structurally complex and provide stable habitats that can shelter a wealth of biodiversity, provided they are managed sustainably.
Thanks to their permanent root systems and abundant leaf litter, tree crops also help prevent soil erosion, boost soil fertility and provide year-round habitats for numerous species. They participate in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by storing carbon, strengthen the connections between fragmented habitats, and mitigate the impact of intensive agricultural landscapes on neighbouring protected areas. On a socioeconomic level, perennial tree crops are often more labour-intensive than their annual counterparts, which provides significant job opportunities, particularly in developing countries where such crops are grown widely.
The article calls for a rollout of regulations, financial incentives and support policies aimed at improving the practices used to grow such crops, to maximize their contribution to global sustainability. "We need bespoke policies tailored to different contexts, from economic incentives to restore natural zones within intensively farmed regions to international regulations in favour of sustainable agriculture in producing countries", says Ignasi Bartomeus, another researcher at the Estación Biológica de Doñana.
This call for action marks a crucial stage in the drive to rethink the role of agriculture in building a fairer, more sustainable future.
Reference
Carlos Martinez-Nuñez, Elena Velado-Alonso, Jacques Avelino, Pedro J. Rey, G. Martijn ten Hoopen. Guy Pe’er, Yi Zou, Yunhui Liu, Philip Antwi-Agyei, Adrien Rusch, Charles Staver, Tharaka S. Priyadarshana, Denis J. Sonwa, Damayanti Buchori, Lucas A. Garibaldi, Elena D. Concepción, Owen T. Lewis, Ivette Perfecto, Ignasi Bartomeus. Tailored policies for perennial woody crops are crucial to advance sustainable development. Nature Sustainability.
Download the publication