- Home
- Our activities, our impact
- Tropical value chains
- Coconut
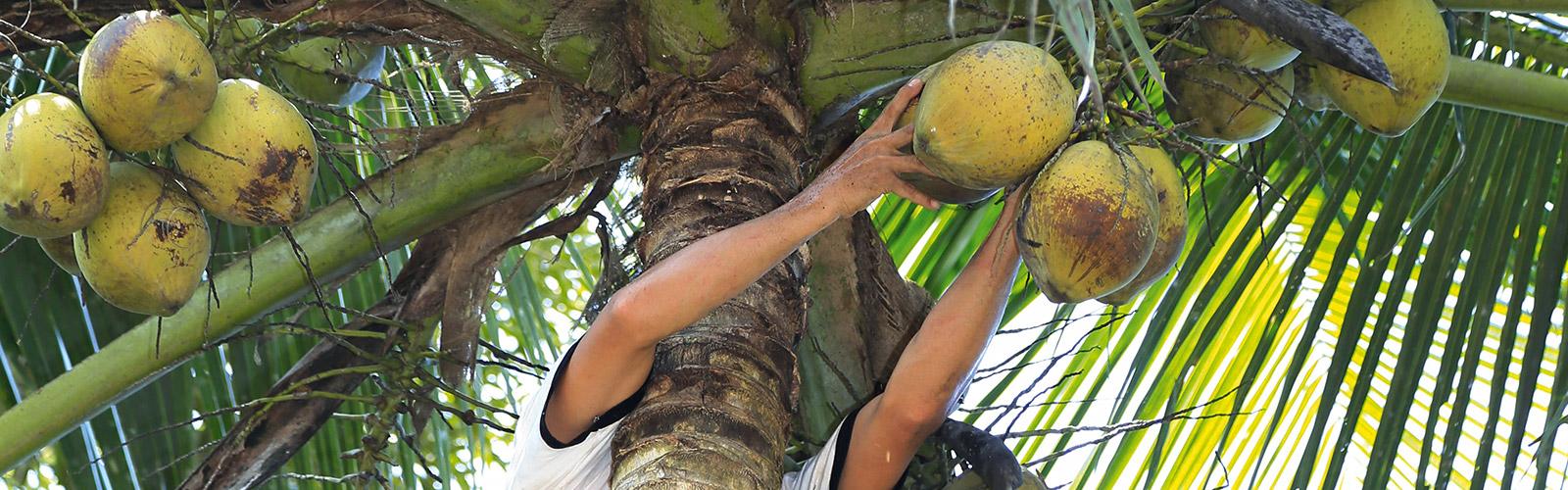

Coconut
The market for "eating" coconuts is booming. However, copra, a vital source of income for many farms, is in decline.
The figures for coconut
86% of the area planted is in Asia and Oceania
96% of farms are small family units of between 0.5 and 4 hectares
84% of global copra output comes from Asia (Philippines, Indonesia, India)
3 million tonnes of copra oil are produced each year
Less than half of that – 1.3 million tonnes a year – is exported; most is consumed in producing countries
The issues
- On an agronomic level, controlling pests and above all lethal viral or phytoplasma diseases (lethal yellowing), which affect ever more countries each year.
- In terms of processing, supporting the development of products with high added value, from a technical, socioeconomic and environmental point of view.
- In the field of genomics, sequencing the coconut genome.