Science at work 23 February 2026
- Home
- Our activities, our impact
- Tropical value chains
- Coffee
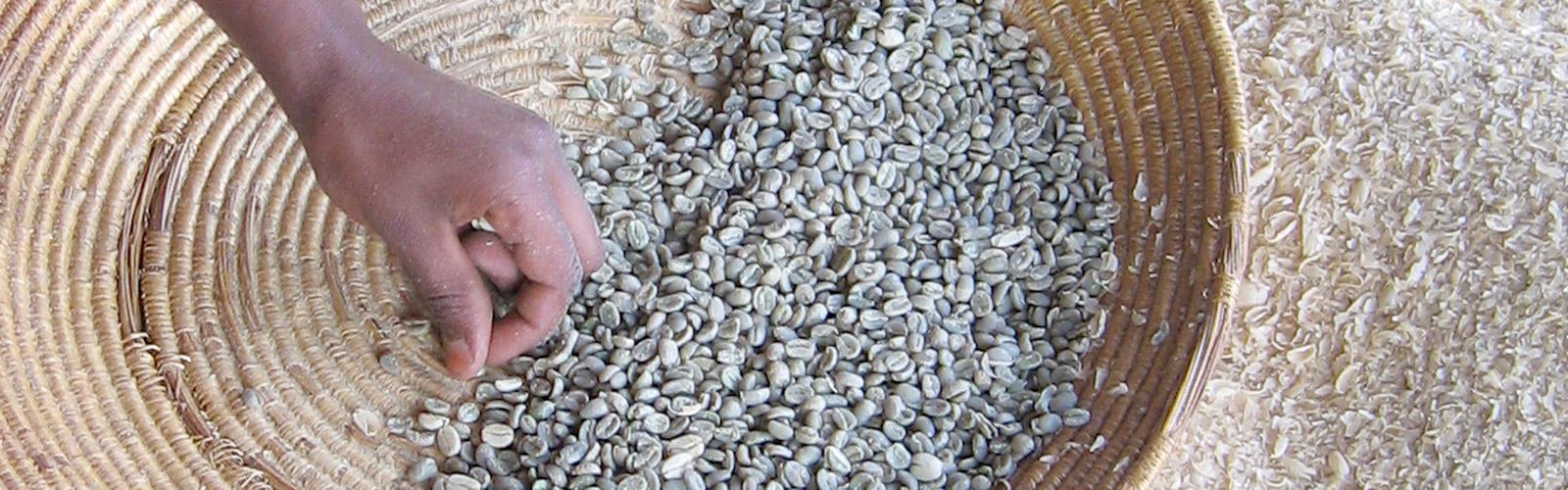

Coffee
CIRAD’s research is aimed at developing and promoting coffee production standards in line with the principles of sustainable development, that are also economically viable.
- Promoting the ecological functions of coffee-based agroforestry systems: land management, landscape development, carbon balance, catchment area protection, biodiversity.
- Fostering ecological intensification through integrated pest management, developing resistant varieties with a broader range of sensorial qualities, and better management of the resources in and ecological services rendered by agroforestry systems.
- Assessing the impact of labels (organic, fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance) on how export supply chains are organized in producing countries.
- Assessing the impact of product diversification on how agroforestry systems function, and on coffee producers’ incomes.
Appraisals
CIRAD’s experts can intervene at production sites or provide one-off support, assistance and advice missions. They also have laboratories and research greenhouses.
- Studies, definition and establishment of trials, varietal and agronomic assessments, economic analyses, prospective analyses, disease surveys and diagnosis, technical support
- Analysis of the conditions for introducing geographical indications or terroirs
- Research and development project design and set-up
- Laboratory analyses: soils, leaves, diseases, paternity, etc.
- Sensorial and chemical analyses of green and roasted coffees
- Mycotoxin analyses
- Product traceability
Expertise
Biodiversity and exploitation of genetic resources
- Genetic resource management, varietal creation, breeding, molecular and cellular biology, physiology
- Seeds and reproduction systems (somatic embryogenesis, mass-produced cuttings, seed gardens)
Optimization of production
- Insect, weed and disease control
- Cropping practices and fertilization
- Production mechanization, rural development and the environment
- Postharvest techniques and analyses
- Coffee promotion (origins, terroirs, etc.)
Modelling of coffee tree functioning
- Computer, mathematical and statistical modelling
- Carbon balance
- Integration of coffee growing into national development operations
Development of sustainable disease resistance management strategies
- Identification of fungal pathogens
- Characterization of resistance sources
- Identification of resistant varieties
- Analysis of disease development in the field
- Taking account of fungal constraints in crop cycles
Products and services
- Products and services centring on coffee
- Rational fertilization software using the soil diagnosis method for coffee: a computer program that facilitates interpretation of chemical analyses, to help agronomists manage soil mineral nutrition in coffee plantings
- New arabica hybrids and rootstock varieties
Analyses
- Near infrared spectroscopy: to identify and authenticate coffees using commercial green and roasted coffee spectral databases compiled by CIRAD
- HPLC, gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, etc: to identify the biochemical and chemical compounds in coffee (caffeine, fats, sugars, trigonelline, chlorogenic acids, diterpenes)
- Analyses of coffee contamination by ochratoxin A: monitoring of processing methods and ochratoxin A titration (ISO 17025)
Training
- Available training on coffee
- Training in near infrared spectroscopy and analysis techniques for interpretation and modelling
- Microbiology training with a view to identifying and culturing the moulds that produce ochratoxin A