- Home
- Worldwide
- CIRAD worldwide
- Projects
- SWM 2 Project
Sustainable wildlife management programme - Phase 2 - SWM2
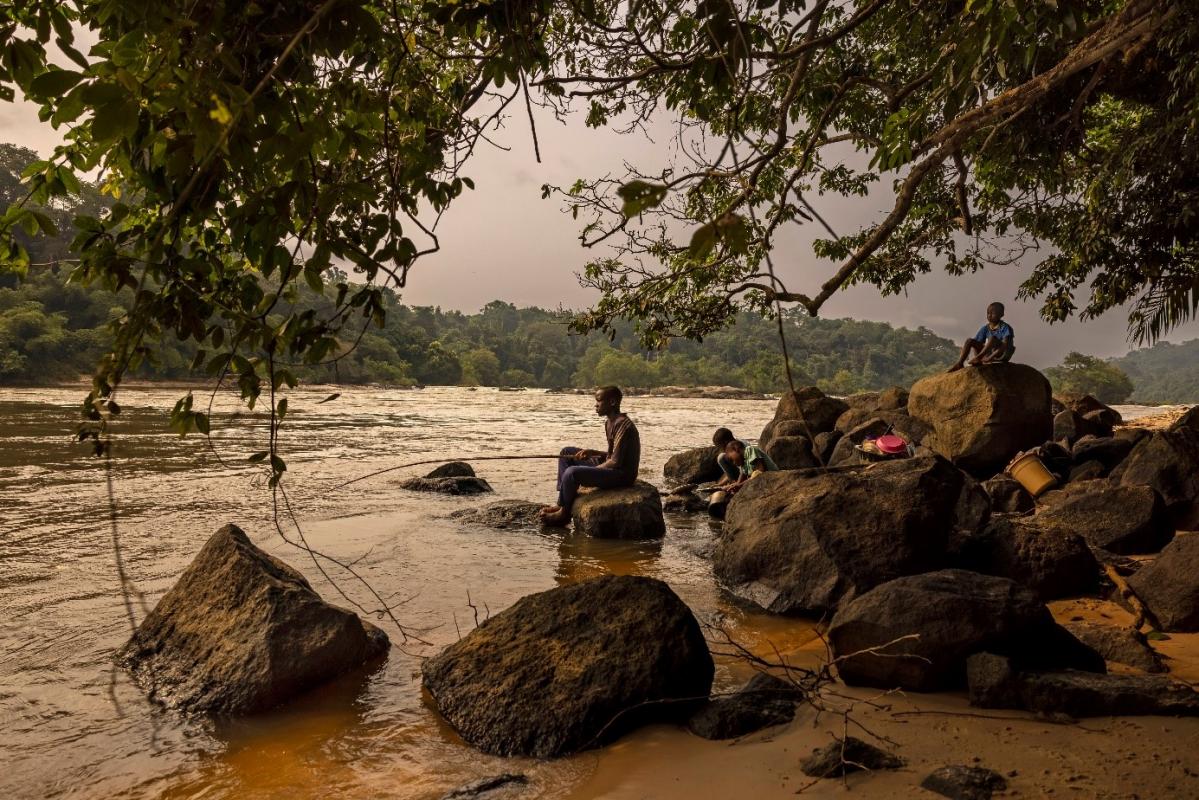

Fishing in Gabon © Brent Stirton/Getty Images for FAO, CIRAD, CIFOR and WCS
Issues
The forests of Gabon have extremely high levels of plant and animal biodiversity. In the Mulundu department, Ogooué-Lolo province, the diverse and abundant wildlife provides an important source of protein and income for the small rural communities living there. However, growing demand for bushmeat from secondary and large cities could affect the availability of resources for these village communities.
In Zimbabwe, the Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area (KAZA) has a wide variety of ecosystems and landscapes. Large scale migrations of megafauna take place there annually. Although the rural communities of Mucheni (Zimbabwe) and Simalaha (Zambia) have different cultures and local governments, they both rely on hunting and fishing for their food and income. However, the livelihoods of these communities are threatened by irregular rainfall, poor soils and human-wildlife conflicts.
Description
In Gabon, the SWM project activities, coordinated by CIRAD in collaboration with the local communities and the Ministry of Water and Forests, consist in fostering the sustainable management of village hunting and the local bushmeat trade while increasing the supply of alternative proteins.
In Zimbabwe, CIRAD conducts activities in the context of the SWM project in cooperation with the governments of Zambia and Zimbabwe. The project continues to encourage the sustainable use of natural resources by Community Conservancies (CCs), especially wildlife and fishing. It also develops alternative sources of protein through livestock farming and aquaculture.
Expected results
In Gabon, the community-based wildlife management model could be extended to other departments and to the priority NaturAfrica cross-border landscapes, such as TRIDOM (Cameroon, Republic of Congo, Gabon). With the legal reform process currently underway, Gabon could become a leading country in sustainable wildlife management by and for communities.
In Zimbabwe, the CC territorial management model, with its inclusive and integrated approach, will be extended in the Binga district, where the local authority wishes to establish further CCs. Scaling up will also take place at the national level on the edges of protected areas in the Zambezi valley and the Lowveld, both of which are target landscapes of the EU Multiannual Indicative Programme 2021-2027 and potential intervention sites for NaturAfrica.
- In Gabon: Centre Interdisciplinaire de Recherche Médicale de Franceville (CIRMF), Institut de Recherche en Ecologie Tropicale (IRET), Ministry of Water and Forests (MINEF)
- In Zimbabwe: Forestry Commission (FC), Zimbabwe Parks & Wildlife Management Authority (ZPWMA), Ministry of Environment, Climate and Wildlife Zimbabwe